Difference between revisions of "Plane nations: Germany"
| Revision as of 09:55, 18 December 2018 Updated tech tree image from 1.4 to 2.0 | Revision as of 10:02, 18 December 2018 comment about tech tree correctness | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | |||
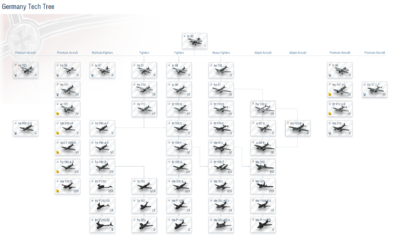
| [[image:Germany_Tech_Tree.png|thumb|400px|2.0 German Plane Tree]] | [[image:Germany_Tech_Tree.png|thumb|400px|2.0 German Plane Tree]] | |||
| }} | }} | |||
| ? | + | Note that the bomber line is missing here, which should be starting at IV (researched from tier III heavy fighter) up to tier VI. | ||
Revision as of 10:02, 18 December 2018

The Luftwaffe developed its own fighter aircraft doctrine and implemented it consistently. German fighters were mainly designed for achieving superiority in the air by way of specially planned airborne operations and “free hunting.”
Preferences were given to aircraft optimized for vertical combat at mid to high altitude. This concept is reflected in the aircraft design of all German tech branches.
German fighters have decent health pools and good firepower. Their auto cannons are usually well built and overheat slowly. Most don't maneuver very well though.
German heavy fighters are the only ones in the game until tier 4. They have medium health pools and are high altitude planes.
German attack aircraft Come into play at tier 4, two tiers after the Soviets. They are faster and more maneuverable than the Russian counterparts but have less hitpoints. Fortunately, all of their Attack Aircraft feature rear-gunners except for the second tier 5 Hs 129 B
Note that the bomber line is missing here, which should be starting at IV (researched from tier III heavy fighter) up to tier VI.
Fighters
Fokker Dr.I Dane podstawowe Państwo Cesarstwo Niemieckie Producent Fokker Typ myśliwiec jednomiejscowy Załoga 1 Historia Data oblotu 5 sierpnia 1917 Lata produkcji 1917-1918 Dane techniczne Moc 110 KM (82 kW) Wymiary Rozpiętość 7,19 m Długość 5,77 m Wysokość 2,95 m Powierzchnia nośna 18,7 m² Masa Własna 406 kg Startowa 586 kg Osiągi Prędkość maks. 166 km/h na wysokości 4000 m Prędkość minimalna 72 km/h Prędkość wznoszenia 5,7 m/s Pułap 6 000 m Zasięg 300 km Długotrwałość lotu 1,5 h Dane operacyjne Uzbrojenie 2 karabiny maszynowe 7,9 mm Użytkownicy
Cesarstwo Niemieckie
Rzuty Rzuty samolotu Commons Multimedia w Wikimedia Commons Fokker Dr.1 – niemiecki samolot myśliwski, trójpłatowiec z okresu pierwszej wojny światowej.
Powstał w odpowiedzi na pojawienie się w lutym 1917 r. trójpłatowca Sopwith Triplane, jednak nie był jego kopią, tylko samodzielnym projektem. Samolot został zaprojektowany przez Anthony'ego Fokkera i szefa warsztatu doświadczalnego zakładów Fokkera Reinholda Platza.
Konstrukcja
Dr.1 był wolnonośnym trójpłatem z kratownicowym kadłubem krytym płótnem, gruby profil płatów i ich niewielka rozpiętość zapewniały mu doskonałą zwrotność i wznoszenie. Jednak trzeci płat zwiększył opór czołowy, w związku z czym samolot z dość słabym silnikiem rotacyjnym o mocy 110 KM rozwijał maksymalnie 165 km/h. Z tego względu nie nadawał się do pościgu za szybszymi dwupłatowcami, był natomiast doskonały w walce kołowej. Jego uzbrojenie to 2 karabiny maszynowe strzelające przez śmigło.
Użycie w lotnictwie Pierwsze dwa egzemplarze maszyny zostały przetestowane przez najlepszych wówczas pilotów myśliwskich: Wernera Vossa i Manfreda von Richthofena („Czerwonego Barona”), których opinia miała decydujący wpływ na wprowadzenie samolotów na front w październiku 1917 r. Wyprodukowano 320 egzemplarzy.
Samolot nie miał bezpośredniego następcy, innych trójpłatów Niemcy seryjnie nie budowali. Zastąpił go Fokker D.VII.
Multirole Fighters
Heavy Fighters
Attack Aircraft
Bombers