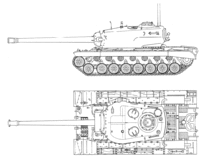
T34

The T34 is an American tier 9 heavy tank. Upon reaching it, it may feel like a downgrade from the T32, as it is literally the same as the T29 when stock. However, it offers increased mobility as you gain experience points, you will eventually gain access to the powerful 120mm T53 gun. Even with this gun, the T34 is a very situational tank. Use caution and strategy when playing this tank; the upgraded turret, mobility, and T53 gun are your best strengths in higher-tier fights.
- The T34 currently leads to the T30. The upcoming 0.7.2 patch will be introducing the M103 as the tier 9 heavy tank replacement for the T34. The T34 will be moved to premium tanks as tier 8. It has not been confirmed if whether the T34 will be available in the store for purchase.
A13 T34 hvy/ModulesA13 T34 hvy/EquipmentA13 T34 hvy/Consumables
Historical Info
By the middle of 1944, combat reports from Europe describing the use of heavy tanks by the Germans stimulated new interest in the development of an equivalent American vehicle. The Pershing medium tank provided an answer to the early model of the German PzKpfw VI Tiger. However, although the latter was still in front line service, it had first been encountered by the US Army during 1943. By 1944, the Germans were introducing even more heavily armed and armored vehicles, like the PzKpfw VIB Tiger II. Although the M26 Pershing was temporarily redesignated as a heavy tank for morale purposes, it clearly did not provide an answer to the problem. On 14 September 1944, US forces recommended development and manufacture of four prototypes for a new heavy tank. Two of these were designated as the heavy tank T29 and were to be armed with the 105mm T5E1 gun. The remaining two were designated as the heavy tank T30 and were to be armed with the 155mm T7 gun.
History
In order to further increase the firepower of the T29 prototype, the US Army undertook design studies in early 1945 to modify the 120mm antiaircraft gun for tank use. These studies indicated that such a weapon, designated as the 120mm T53 gun, would have armor piercing performance superior to that obtainable with either the 105mm T5E1 or the 155mm T7. The new 120mm gun had a muzzle velocity of 3150 feet per second with a 50-pound solid shot, and development was in progress on a lightweight HVAP round with a muzzle velocity of 4100 feet per second. On 17 May 1945, the US Army recommended that two of the T30 prototype tanks be armed with the 120mm gun and redesignated as a heavy tank T34. This action was approved on 31 May.
Technical info
Originally, the T29, T30, and T34 heavy tanks were all to be powered by the Ford GAC engine. However, after VJ-day, the program was modified to permit the evaluation of other new power plants, and the military characteristics of the T30 were changed to specify the Continental AV-1790 engine, which was still coupled to the cross-drive transmission. On 7 November 1946, US Army recommended that the two T34 prototypes use the T30 chassis and that the characteristics of the T34 also be changed to specify the Continental engine. Prior to this, it had been intended to use the modified Allison V-1710 aircraft engine. However, use of the two chassis diverted from the T30 prototype program was recommended to reduce costs.The T34 prototypes were similar in appearance to the T29 and T30 tanks, except for the longer barrel of the 120mm gun. Like the T29, the combination gun-mount was fitted with two coaxial .50 caliber machine guns on the left side of the cannon. The heavier weight of the 120mm gun required the welding of an additional four inches of armor onto the rear of the turret bustle to balance the long cannon. On the pilot tanks, this provided an obvious identification point. No doubt, if the tank had gone into production, the rear of the turret casting would have been thickened up and it would not have been so easily detected.
Like the 120mm antiaircraft gun from which it was developed, the T53 cannon used separated ammunition. Thus, the ammunition stowage in the T34 was similar to that in the T29 and T30 tanks, which used the same type of round. The 120mm projectile and cartridge case each weighed about 50 pounds, so the problem of the two loaders in handling the ammunition was not as severe as with the 155mm gun in the T30. However, another problem arose during test firing at Aberdeen and Fort Knox: tests revealed that dangerous concentrations of smoke and carbon monoxide formed inside the turret after firing a few rounds. Also, flarebacks hospitalized at least two men at Fort Knox, and singed the hair and eyebrows of several others there and at Aberdeen. These flarebacks were caused by unburned powder gases in the gun tube being sucked back into the turret by the pumping action of the ejected cartridge case. A flash resulted when these hot gases mixed with the oxygen in the turret.
To prevent the flarebacks, a bore scavenging system was developed using compressed air to sweep out the gun tube before the breech opened. However, this complex arrangement resulted in leaks at the various valves, and required space for an air compressor and reservoir. A simple solution to the problem was the installation of an aspirator-type bore evacuator. Previously tested on the 90mm T15E4 and M3E4 cannons, it consisted of a cylindrical chamber fitted around the gun barrel just behind the muzzle. Holes angled towards the muzzle were drilled along the barrel wall and connected the bore with the evacuator chamber. As the projectile moved down the tube past these evacuator ports, the high gas pressure in the bore also pressurized the evacuator chamber. Once the projectile cleared the muzzle, the pressure in the bore dropped rapidly and the high pressure remaining in the evacuator chamber caused the formation of high velocity gas to jets from the evacuator ports. These jets angled toward the muzzle, sweeping the powder gas out of the bore before the breech opened. Tests at Aberdeen and Fort Knox showed that this simple device was extremely effective and it became a standard feature of new tank guns.
T-series Prototypes
The T29, T30, T32, and T34 series of tanks were used to evaluate numerous experimental components after World War II. Although too late for the war for which they were designed, they provided invaluable service in developing these components for later tanks. Much of the work making the early AV-1790 engine and the CD-850 transmission a reliable power package utilized these tanks. Later, these prototypes were used in the development of other power train components, such as the XT-1400 transmission, which was tested in the T30.
| Mk.VII | M6 | T28 | T29 | T30 | T32 | T34 | M103A2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Crew | 8 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 5 |
| Lenght | 10,43m | 8,43m | 11,12m | 11,56m | 10,9m | 10,83m | 11,77m | 11,23m |
| Width | 3,66m | 3,12m | 4,54m | 3,8m | 3,8m | 3,76m | 3,8m | 3,63m |
| Height | 3,12m | 3,00m | 2,86m | 3,22m | 3,22m | 2,81m | 3,22m | 3,56m |
| Weight | 39,5t | 57,4t | 86,3t | 64,25t | 64,74t | 54,5t | 65,2t | 58,1t |
| Engine power |
Liberty 338hp |
G-200 960hp |
GAF 500hp |
GAC 770hp |
AV1790 810hp |
GAC 770hp |
AV1790 810hp |
AV1790 750hp |
| Max. speed | 8,8km/h | 35km/h | 12,8km/h | 35km/h | 35km/h | 35km/h | 35km/h | 37km/h |
| hull armour (angle) |
12mm (28) |
83mm (30) |
305mm | 102mm (54) |
102mm (54) |
127mm (54) |
102mm (54) |
127mm (60) |
| side armour | 12mm | 70mm | 152mm | 76mm | 76mm | 76mm | 76mm | 51mm |
| Turret armour (mantlet) |
16mm | 83mm (102mm) |
- | 178mm (279mm) |
178mm (279mm) |
298mm (298mm) |
178mm (279mm) |
127mm (254mm) |
| top armour | 6-10mm | 25mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm | 38mm |
| bottom armour | 6-8mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 25mm | 38mm |
| Gun | 2x57mm Hotchkiss |
75mm M7 37mm MB |
105mm T5E1 |
105mm T5E2 |
155mm T7 |
90mm T15E2 |
120mm T53 |
120mm M58 |
| Secondary armament |
5x7,62mm Hotchkiss |
2x12,7mm HB M2 2x7,62mm M1919A4 |
12,7mm HB M2 |
3x12,7mm HB M2 7.62mm M1919M4 |
2x12,7mm HB M2 7.62mm M1919M4 |
12,7mm HB M2 2x7.62mm M1919M4 |
3x12,7mm HB M2 7.62mm M1919M4 |
3x12,7mm HB M2 7.62mm M37 |
| Light Tanks | T1 Cunningham • M2 Light Tank • T1E6 • T2 Light Tank • T7 Combat Car • M22 Locust • M3 Stuart • MTLS-1G14 • M5 Stuart • M24 Chaffee • T21 • T71 |
| Medium Tanks | T2 Medium Tank • M2 Medium Tank • M3 Lee • M4 Sherman • M4A2E4 Sherman • M7 • Ram II • M4A3E2 Sherman Jumbo • M4A3E8 Sherman • T20 • M26 Pershing • T23 • T26E4 Super Pershing • T69 • M46 Patton • T54E1 • M48A1 Patton • M60 |
| Heavy Tanks | T1 Heavy Tank • T14 • M6 • T29 • M6A2E1 • T32 • T34 • M103 • T57 Heavy Tank • T110E5 |
| Tank Destroyers | T18 • T82 • M8A1 • T40 • M10 Wolverine • T49 • M18 Hellcat • M36 Jackson • T25 AT • T25/2 • T28 • T28 Prototype • T30 • T95 • T110E3 • T110E4 |
| Self-Propelled Guns | T57 • M7 Priest • M37 • M41 • M44 • M12 • M40/M43 • M53/M55 • T92
|