Renault FT

The Renault FT is a French tier 1 light tank. It is the first French tank available to the player. It has good acceleration, but very poor top-speed. The available guns have only sub-par damage-potential, but a very high firing-rate. The armor is among the thickest in its tier.
- The Renault FT leads to the Hotchkiss H35 and the D1.
F01 RenaultFT/ModulesF01 RenaultFT/EquipmentF01 RenaultFT/Consumables
Pros and Cons
Pros:
- High hull armor
- Highest turret armor for its class
- Best radio in its tier
Cons:
- Very underpowered starting engine
- Poor speed and maneuverability
Combat Effectiveness
The FT can play out its strengths on maps with more narrow sections, where you can essentially be a roadblock for enemy tanks. Something to note that the gun elevation is as good as the T57's, but the gun depression is very poor (i.e. it's good at shooting up, but bad at shooting down).
Early Research
- Make upgrading the engine your first priority.
- Save the radio for last.
- Go from there.
Suggested Equipment (if any)
Historical Info
One of the qualities of the machine was to be its ability to descend into the gully and out, instead of trying to climb over. From February 22, 1917, an initial order of 150 tanks gunners had passed, soon followed by a request from General Petain 3350 for additional copies. The official test of the tank called Renault FT took place April 9, 1917, with the immediate result to increase to 1,000 the number of copies ordered in addition to the first 150. During the second decade of July, they tried the turret with the piece of 37 mm which had decided to arm 650 tanks. It was assigned to several production companies and a total of 7820 FT tanks were ordered with 3940 the firm Renault. At the time of the armistice, only 3177 copies had been delivered (of which several hundred were destroyed in combat) but production continued, so that in 1921 there were 3728 (2100 armed with machine guns, 1246 37 mm cannon, 39 cannon, 75 mm, 188 radio, without armament and 155 others classified as "school"). The unit price was around 56 000 francs at the time.
The technique
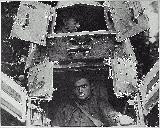
The design included a light tank shell door, made of plates bolted to the profiles. The pads of the track, with a length of 340 mm, guaranteed a good grip on any terrain.
Inside the box was divided into two distinct parts: fighting compartment and engine compartment. In the first pilot was sitting on a seat with adjustable back and, in the turret, the gunner used the machine gun or cannon. You can find this compartment with two doors that formed the roof and the beach front. Originally, there were no other openings, but the prototype was equipped with a hatch at the rear of the turret hatch, which was converted into a double door. The pilot's visibility was provided by three slots of sight.
Motor, gears, radiator and fuel tank were accessible only from outside. You could check by lifting the flaps on the roof of the engine compartment. The propellant was a 4-cylinder equipped with a Zenith carburetor supplied with gasoline even if the tank was strongly inclined by a diaphragm pump.
The magneto ignition was switched on and manually (by means of a crank) was done from both the outside and inside the tank. The shield vulnerable parts were 16 mm thick. or semi-automatic gun Puteaux of 37/21 (with 240 explosive projectiles, 12-shot). To facilitate the crossing of trenches, the Renault FT was provided with a removable tail which he could rely.
In 1939 the tank FT is totally obsolete and its use is intended only for side missions: protection of airfields and depots, monitoring hot spots. The disastrous campaign of spring 1940 will force the French army to challenge the venerable FT front line crews and their selfless sacrifice to delay Nevita defeat.
The tanks used in 1940 are characterized by the presence of tricolor cockades affixed to the body and the turret. Technically these are exactly the same as those that have taken place in 1918.
SPECIFICATIONS Manufacturer: Renault (1850), Berliet (800), SOMUA (600), Delauney-Belleville (280) Production period: 1917 - 1920 Type: Light Tank Crew: 2 men Length (m): 4.95 m Width (m): 1.74 m Height (m): 2.14 m Combat Weight (kg): 6700 Maximum armor: 22mm Radio equipment: none WEAPONS Main armament: a Hotchkiss 8mm machine gun or a 37mm SA18 gun Rotation (degrees): 360 ° Elevation (degrees): + 35 ° - 20 ° MOBILITY Engine: Renault Type & Capacity: 4.48 l 4 cyl Power (max.): 35 hp Power / weight ratio: 5 hp / t Transmission: 4 speed Fuel: Petrol Autonomy (km): 35 Consumption (litres/100km): 30 Fuel Capacity (liters): 100 Road speed: 7.5 km / h Tracks: 32 skates Track Width: 0.34 Ground clearance (inches): 0.43 Slope (degrees): 10 Vertical Obstacle (m): 0.60 Fording (m) 0.70
Crossing (m): 1.35